Which SMTP Port to Use? Understanding ports 25, 465, & 587

It’s a common question that we receive here at Sinch Mailgun about SMTP port numbers. To ensure connectivity to our Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) endpoint, Mailgun offers multiple SMTP port options, but which one should you use to send email messages? We’ll take a historical look at each SMTP port and then we’ll discuss today’s methodology for outgoing mail usage. If you’re not a history buff, go to “Today’s Usage” for the most common SMTP ports.
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol – put simply, it’s the process by which emails are sent across the internet. Message data is sent out and the traffic is directed into ports. Once message data travels successfully through a port, other email authentications are used to validate the messages and either deliver them to the inbox, reject them, or direct them to the spam folder.
SMTPS is more secure than SMTP in the same way that HTTPS is more secure than HTTP. In the earlier days of the internet www.http was the standard beginning to an email address. But it became easy for spammers and spoofers to intercept sensitive data. HTTPS = HTTP + SSL, or secure socket layer, which is an internet address’s extra layer of authentication. SMTPS is SMTP + TLS, or transport layer security, which uses encryption and authentication to further protect SMTP.
TLS uses a digital signature to verify the origin of traffic. In email we talk a lot about authentication to verify a senders identity with protocols like SPF or DKIM. Instead of verifying who sends a message, TLS verifies by where email traffic comes from. If the origin in the signature matches the actual origin, the data is allowed through. The default SMTP port for SMTPS is port 587, but more on that in a bit. Before we talk about default ports, we first have to know what an SMTP port is.
Ports are endpoints that individual servers use to connect to a network and retrieve data. Think of it like an old school switchboard with a technician plugging the incoming call into a jack to connect it to a specific phone. An SMTP port is a port designed to direct email through a network to its recipient.
The most important SMTP ports are:
The thing is, not all SMTP ports are equal. Choosing the wrong one could have negative consequences and reflect poorly on you as a sender.
There are many ports to choose from, but only a few that you might want to use. Like with anything technical, where we started is not where we are now. When the SMTP protocol was first published in 1981 (the same year Lionel Richie’s Endless Love topped the charts – for perspective) it didn’t take long before the first port, port 25 was put into place to manage message traffic.
What about the rest of the SMTP ports? How many other ports were launched over time and have they evolved? Many have, and some have even been depricated. When it comes to ports, there are many. Here’s our breakdown – or “port reduction” if you will. Sorry, we couldn’t resist.
The first port, port 25, was implemented as the primary message transmission channel to help mitigate against attacks like man-in-the-middle. It came out of a 1982 request from the University of Southernn California to the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) who are the overlords of all protocols that control movement across the internet.
Ironically, SMTP port 25 has since become favored by spammers because of its support for open relay.
SMTP port 25 continues to be used primarily for SMTP relaying. SMTP relaying is the transmission of email from email server to email server.
In most cases, modern SMTP email clients (Microsoft Outlook, Mail, Thunderbird, etc.) shouldn’t use this port. It is traditionally blocked by residential ISPs and Cloud Hosting Providers, to curb the amount of spam that is relayed from compromised computers or servers. Unless you’re specifically managing a mail server, you should have no traffic traversing this port on your computer or server.
In December of 1998, after port 25 started to get spammy, R. Gellens and J. Klensin submitted RFC 2476 in support of adding a new specification for internet email communications. The RFC proposed a split of the traditional message submission and message relay concept.
The RFC defined that message submission should occur over port 587 to ensure new policy and security requirements don’t interfere with the traditional relay traffic over message relay port 25.
Port 587 is the default mail submission port. When an email client or outgoing server is submitting an email to be routed by a proper mail server, it should always use SMTP port 587 as the default port.
This port, coupled with TLS encryption, will ensure that email is submitted securely and following the guidelines set out by the IETF.
All Mailgun Send customers should consider using port 587 as their default SMTP port unless you’re explicitly blocked by your upstream network or hosting provider.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reassigned a new service to this port, and it should no longer be used for SMTP communications.
Because port 465 was once recognized by IANA as valid, there may be legacy systems that are only capable of using this connection method. Typically, you will use this port only if your application demands it. A quick Google search, and you’ll find many consumer Inbox Service Providers’ (ISPs) articles that suggest port 465 as the recommended setup. However, we do not recommend it, as it is not RFC compliant.
Interestingly, port 465 was never published as an official SMTP transmission or submission channel by the IETF. Instead, the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), which maintains much of the core internet infrastructure, registered port 465 for SMTPS. The purpose was to establish a port for SMTP to operate using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). SSL is commonly used for encrypting communications over the internet.
The port was assigned for about one year before it was revoked in support of securing SMTP communications using Transport Layer Security (TLS). The nail in the coffin was a new protocol command “STARTTLS,” introduced in RFC 2487. This command allows SMTP servers to communicate over existing ports by advertising whether the destination server supports TLS encryption. If so, the sending server can upgrade the connection using the “STARTTLS” SMTP command.
Mailgun supports TLS connections, which you can verify by connecting and issuing an “ehlo” from a command line interface. The resultant “250 STARTTLS” confirms the endpoint accepts TLS connection requests.
u003e telnet smtp.mailgun.org 587rnTrying 50.56.21.178... rnConnected to smtp.mailgun.org. rnEscape character is '^]'. rn220 ak47 ESMTP ready rnu003e ehlo blog.mailgun.comrn250-ak47 rn250-AUTH PLAIN LOGIN rn250-SIZE 52428800 rn250-8BITMIME rn250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES rn250 STARTTLS
You can test using the same command sequence on any SMTP server. Try Gmail or Yahoo, “telnet gmail-smtp-in.l.google.com 25” or “telnet mta7.am0.yahoodns.net 25”.
This port is not endorsed by the IETF nor IANA. Instead, Mailgun provides it as an alternate port, which mirrors port 587, in the event the above ports are blocked. Because 2525 is a non-traditional high port number, it is typically allowed on consumer ISPs and Cloud Hosting providers, like Google Compute Engine. If you’ve tried the above ports, but experience connectivity issues, try port 2525. This port also supports TLS encryption.
When you start talking about protocols, you know the specifics are going to matter. SMTP is no different. Your port depends on what type of sender you are.
Most used ports:
| Port | Use case |
|---|---|
| Port 25: The standard port | Use for non-encrypted connections. Still thought of as the standard SMTP port, most residential ISPs and hosting providers block port 25 due to heavy spam traffic. |
| Port 465: The TLS port | Use if your application or company require. Port 465 is a port that carries out message submission over Implicit TLS protocol. |
| Port 587: The default port | Use for your business or for secure connections. Port 587 is the default SMTP port, most businesses use this port. |
Alternative ports:
| Port | Use case |
|---|---|
| Port 80: The HTTP port | Use as the default port for unencrypted webpages. Port 80 is used to send and receive web-based communications and HTML data and allows HTML data to remain in plain text, vs. Port 443 where it would be encrypted. |
| Port 443: The SSL port | Use to get to an HTTPS address. When you send a message, SMTP transmits messages to a specific address for processing. Port 80 is use to open an HTTP address, port 443 is used for HTTPS, or addresses that have SSL security. (The ‘s’ in HTTPS) |
| Port 588: The secondary email port | Use if you require TLS encryption. Both ports 587 and 588 can be coupled with TLS encryption for add data privacy and security. |
| Port 2525: The alternate port | Use as an alternate if port 587 is blocked. Mailgun provides an alternate in port 2525 for situations when standard ports are blocked. Most ESPs support port 2525. |
Using the right port helps ensure delivery and supports your sender reputation. But watch out, some ports have evolved to have a bad reputation of their own – and using these ports could keep you out of the inbox.
Different ports are associated with different security measures, so choosing the right one is key to ensure you’re protecting your email communications.
Some ports transmit encrypted messages, while other ports remain open for all types of traffic. The port you use may be determined by the security standards of your organization or by the sensitive contents of the messages you send.
| Port | Best For | Security | Recommended Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | Server relay | Basic | Legacy systems only |
| 587 | Message submission | TLS support | Modern email sending |
| 465 | Legacy systems | Implicit TLS | When specifically required |
| 2525 | Alternative option | TLS support | When other ports are blocked |
If you’re looking into SMTP, chances are you’re going to come across SMTPS. SMTPS is more secure than SMTP in the same way that HTTPS is more secure than HTTP. In the earlier days of the internet, www.http was the standard beginning to an email address. But it became easy for spammers and spoofers to intercept sensitive data.
In our table above we break down the basic security protocols and primary uses of SMTP ports, but let’s dig a little deeper in what makes these ports secure and why you should avoid some.
How does SMTPS differ from end-to-end email encryption?SMTPS encrypts emails during their transmission across servers but does not provide end-to-end encryption. End-to-end encryption methods like PGP or S/MIME ensure that only the sender and recipient can access the email content, providing a higher level of security.
How SMTPS enhances security
Choosing the right SMTP port also helps ensure you have strong deliverability. SMTP is the most used protocol by mail servers to communicate, but that doesn’t mean they’re interchangeable. Some ISPs may block certain ports, like port 25 to defend against spam, and default to another port, like port 587 that supports encryption.
Adding authentication protocols like SMTP AUTH can help improve your message delivery, but deliverability is a multi-ingredient pie. Everything from your message content to your authentication can impact your sender reputation and overall deliverability rate.
In order to determine which port is the best for you, let’s cover the most popular ports and the traffic they transmit.
When your email client can’t establish a connection to the SMTP server within the expected timeframe. This often occurs due to network issues, firewall restrictions, or when the server is experiencing high load.
These happen when the credentials provided (username/password) don’t match what the SMTP server expects, or when using the wrong authentication method. Most commonly occurs after password changes or when using outdated credentials.
ISPs or firewalls may block specific SMTP ports, especially port 25, as a spam prevention measure. If you’re experiencing connection issues, try switching to port 587 or 2525 as alternatives.
Problems occur when there’s a mismatch between the TLS versions supported by your client and the SMTP server, or when certificates are invalid or expired. Usually resolved by updating your TLS configuration or ensuring proper certificate management.
POP (Post Office Protocol, with the latest version being POP3) and IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) are two of the very first protocols developed on the consumer internet that allowed for email clients – like Outlook, Thunderbird and others – to retrieve mail from a mail server.
The ports typically used for POP are TCP ports 110 and 995, and for IMAP are TCP ports 143 and 993, for insecure and secure sessions respectively. They were each good at doing different things, like reflecting the state of an email back to the server (whether it was read, flagged, or marked as junk), or for preserving a copy of the message on a local machine for easy offline access. The latest version of POP, POP3, can be used with or without SMTP.
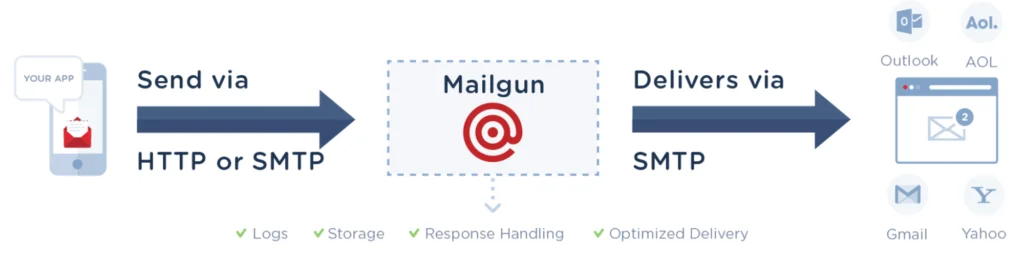
SMTP has been around for years, and many folks ask us whether they should use SMTP or Mailgun’s API endpoint. Deciding whether you should use an email API or SMTP to send your emails might not be an easy choice.
We certainly recognize there is some level of vendor lock-in associated with building around an API. However, SMTP is extremely “chatty” and may lead to less performant mail submission to Mailgun.
For example, consider the typical TLS mail conversation between my computer and Mailgun’s SMTP endpoint:
u003e openssl s_client -starttls smtp -crlf -connect smtp.mailgun.org:587rn250 STARTTLS rnu003e ehlo blog.mailgun.comrn250-ak47 rn250-AUTH PLAIN LOGIN rn250-SIZE 52428800 rn250-8BITMIME rn250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES rnu003e AUTH PLAIN AHBvc3RtYXN0ZXJAc2FtcGxlcy5tYWlsZ3VuLm9yZwAza2g5dW11am9yYTU=rn235 2.0.0 OK rnu003e MAIL FROM:u003ctest@samples.mailgun.orgu003ern250 Sender address accepted rnu003e RCPT TO:u003crecipient@samples.mailgun.orgu003ern250 Recipient address accepted rnu003e DATArn354 Continue rnu003e This is a test of SMTP over port 587.rnu003e .rn250 Great success rnu003e QUITrn221 See you later. Yours truly, Mailgun
As you can see, the above communication is quite cumbersome with lots of back and forth between sender and receiver. We open a connection to the SMTP server, issue the EHLO command, authenticate, set the MAIL FROM, set the RCPT TO, DATA command, send the data, period to close, and finally receive confirmation the message was queued.
Compare this with an HTTPs payload:
u003e openssl s_client -connect api.mailgun.net:443rnu003e POST /v2/samples.mailgun.org/messages HTTP/1.1rnu003e Authorization: Basic YXBpOmtleS0zYXg2eG5qcDI5amQ2ZmRzNGdjMzczc2d2anh0ZW9sMA==rnu003e Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencodedrnu003e Content-Length: 126rnu003e rnu003e from=test%40samples.mailgun.orgu0026to=recipient%40samples.mailgun.orgu0026subject=Testingu0026rnu003e text=This+is+a+test+of+HTTP+over+port+443!rnHTTP/1.1 200 OK
Here, we initiate a connection, pass the HTTP POST payload and receive a 200 OK from the API endpoint. We don’t have to issue a sequence of commands and wait for a response from the server after each command.
To learn more, check out our Documentation for more info, or contact us and we can answer any questions you may have about SMTP ports or our email services.